Débora Lopes Bunzen Mayer; Juliana Gusmão de Araújo; Mariana de Carvalho Leal; Silvio da Silva Caldas Neto; Rafael Figueiredo Ataíde; Roberto José Vieria de Mello
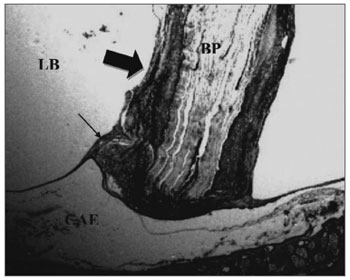
Figure 1. Experimental group at 8 weeks - Microphotography of the tympanic membrane, thickened at the point of contact; sugar cane biopolymer. Surrounded moderate subacute exudate; the biomaterial. BP= sugar cane biopolymer; LB= bulla lumen; CAE= external ear canal; thick arrow = inflammatory reaction; thin arrow =malleus. HE (40x magnification).
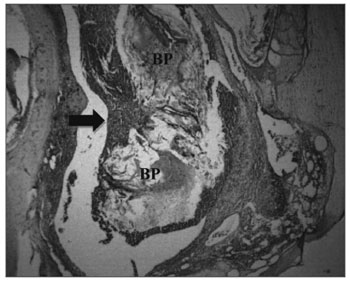
Figure 2. Signs of biomaterial absorption - Microphotography of the membrane's structural disorganization; sugar cane biopolymer; and its partial absorption, seen in the tympanic bulla at 8 weeks; BP= sugar cane biopolymer; thick arrow = inflammatory exudate. HE (40x magnification)
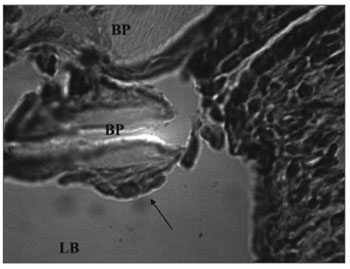
Figure 3. Experimental group chronic reaction - Microphotography of a sugar cane biopolymer membrane having been engulfed by giant cells; foreign body type; BP= sugar cane biopolymer. LB= bulla lumen. Thin arrow =giant cell. HE (1000x magnification).
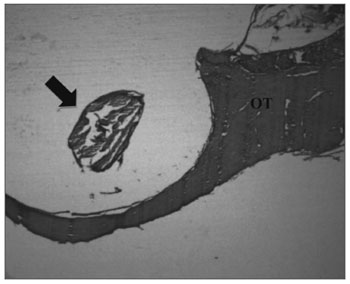
Figure 4. Experimental group with 12 weeks - Microphotography of the sugar cane biopolymer membrane; on the tympanic bulla without signs of inflammatory reaction. OT= temporal bone; broad arrow = sugar cane biopolymer. HE (40x magnification).
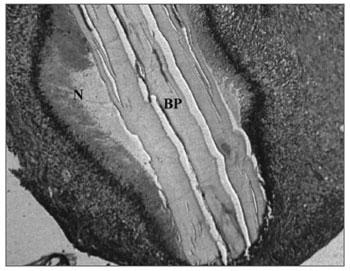
Figure 5. Experimental group with 4 weeks - Microphotography of the subacute exudate of moderate degree around the sugar cane biopolymer membrane; BP= sugar cane biopolymer. N= cell necrosis. HE (100x magnification)
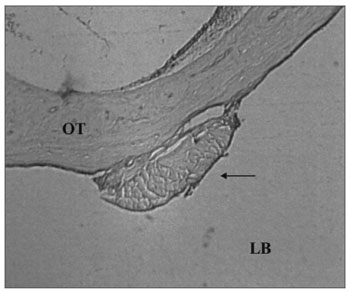
Figure 6. Control Group. Microphotography of the fascia adhered to the tympanic bulla mucosa. LB= bulla lumen; OT = Temporal bone; thin arrow= fascia. HE (100x magnification).


